Diamond Cut and Diamond Shape Buying Guide
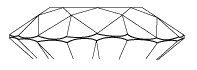
Diamond Anatomy
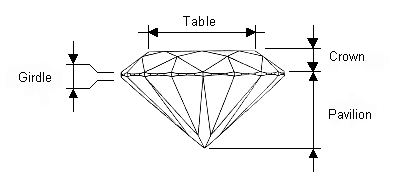
Diamond has 4 great parts:
- Table
- Crown
- Girdle
- Pavilion

A Round Brilliant Cut Diamond has between 57 and 58 facets (depending on whether the culet was polished into a facet or closed to a point):
- Table: 1 facet.
- For the crown: 8 bezels, 8 stars and 16 upper girdle facets.
- For the pavilion: 8 pavilions and 16 lower girdle facets.
- Culet: 1 or 0 facet (if no culet facet). Also, in higher quality goods the girdle is frequently faceted, but these facets are not counted in the total.
Shape and Cut
The Round Brilliant Shape
 |
 |
Pictures of the Most Popular Diamond Shapes
Videos of the Most Popular Diamond Shapes:
Calculating brilliant cut diamond: diameter/weight
Gallery of images of various shapes and cuts: 77 listed shapes
Proportions
The tool used to measure the proportions of a diamond is a proportionscope.
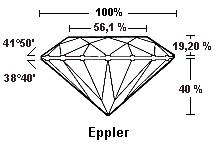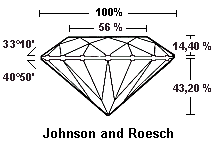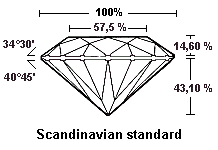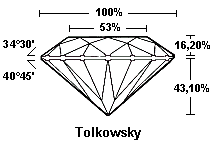
It is necessary to consider all the proportions and not only some of them. An angle of crown too large or too small is indicated in remark.
An open culet indicates a poor stone (except in the case of the old cuts).
In melee, thick rondists indicate not very interesting stones.
Many professionals consider the cut the most important diamond characteristic because even if a diamond has perfect color and clarity, a diamond with a poor cut will have dulled brilliance.
For those how wish more information regarding the proportions of the brilliant cut, they will know that in 1919, Marcel Tolkowsky published « Diamond Design » in which he describes his research on the proportions of the brilliant cut. You can click on this link and search his work: Tolkowsky
The « ideal » Diamond Cut:
It is a very vast subject, which divides the professionals still today. To obtain the maximum of brightness, fire, « life », a diamond must be cut according to certain dimensions and proportions. The diamond cutters must carefully consider the optical properties of each diamond to determine its optimal size.
Brilliance of a diamond following the proportions of its cut:

Ideal Cut: light is correctly reflected. Diamond has a beautiful brilliance.
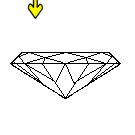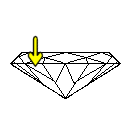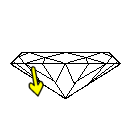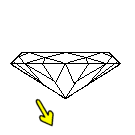
Too Shallow: light is lost out the sides causing the diamond to lose brilliance.

Too Deep: light escapes out the bottom causing the diamond to appear dark and dull.
To obtain an ideal cut, the 3 principal elements, are:
1) Total Depth %:
The height of the stone is divided by the diameter in rounds or by the width in all other shapes. Say the stone measures 6.52 - 6.56mm x 3.92mm, the total depth is 3.92mm ÷ 6.54mm = 59.93%. Ideal round diamonds should have a depth of 59%-62.50%.
2) Table Percentage (%):

Only round diamonds have a standard for table size. In round diamonds for a diamond to be recognized as an ideal cut the table must be relatively small. It must fall between 53% and 57%.
3) Girdle thickness:

The best girdle range for a diamond to fit in the ideal cut category for rounds is anywhere between « Thin » and « Slightly Thick ». The girdle could be Thin, Medium, Slightly thick or any combination of the three, such as « medium to slightly thick ». The various graduations thickness of the rondist are: Extremely thin, Very thin, Thin, Medium, Slightly thick, Thick, Very thick and Extremely thick.
| Girdle Thickness | ||||||||
| Extremely thin | Very thin | Thin | Medium | Slightly thick | Thick | Very thick | Extremely thick | |
| Extremely thin | GD | VG | VG | VG | VG | VG | GD | FR |
| Very thin | VG | VG | VG | VG | VG | GD | FR | |
| Thin | EX | EX | EX | VG | GD | FR | ||
| Medium | EX | EX | VG | GD | FR | |||
| Slightly thick | EX | VG | GD | FR | ||||
| Thick | VG | GD | FR | |||||
| Very thick | GD | FR | ||||||
| Extremely thick | FR | |||||||
| FR = Fair --- GD = Good --- VG = Very Good --- EX = Excellent | ||||||||
4) Others :
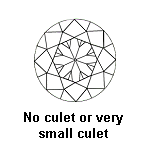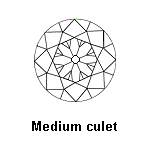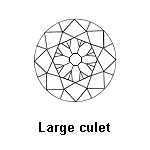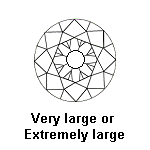
Other elements are important, such as the culet size. The culet size is listed on a certificate and your diamond’s culet should be pointed (no culet), very small, small or medium because these are not visible to the naked eye. The graduations of the culet size are: No Culet, Pointed, Very Small, Small, Medium, Large, Very large and Extremely large. Avoid the culets equal or lower than « Large » which when you look at diamond by the table are very visible with the naked eye.
GIA Culet Size:
| Culet Size | Grade |
| None | Excellent |
| Very small | |
| Small | |
| Medium | Very Good |
| Slightly large | Good |
| Large | |
| Very large | Fair |
| Extremely large | Poor |

The girdle of diamond can be faceted, polished or rough. Diamonds which has a very beautiful cut have often the faceted girdle. A diamond cutter must work from additional time to facet it, which is not always economically profitable. A faceted girdle does not improve quality of diamond. The GIA evaluates only the thickness of the girdle and not its appearance.
Finish of a Diamond
Symmetry of a Diamond
The estimate of « symmetry » results from the observation from:
- The good alignment of the facets.
- The symmetry of the facets.
- The centering of the culet.
- The centering of the table.
A diamond can have good symmetry and poor proportions.
Some examples of symmetry defects:
Eccentric table
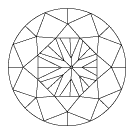
Eccentric culet
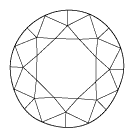
Deformed girdle
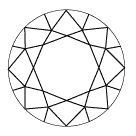
Deformed facet
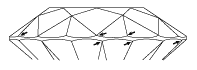
Misalignment of the crown and the pavilion
Undulated girdle
Polish of a Diamond
The estimate of the « polish » results from the observation from:
- The presence of more or less polish lines.
- The presence of stripes. If the stripes are too numerous, they are mentioned in remarks.
The estimate of symmetry and polished results in:
- Excellent
- Very good
- Good
- Fair
- Poor










